This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
March 23, 2020
How Cisco and Other Leading Companies are Transitioning to Net Zero in 2020
SR Inc’s 1st Quarter Symposium Includes Discussion on How Companies Can Commit to and Achieve Bold Sustainability Goals in a Cost Positive Manner
Following our last post on the first half of the Q1 symposium webinar, this post reviews the second half of the meeting and how our Member-Clients are transitioning to net zero operations in 2020. The discussion included a review of what has changed in the realm of net zero operations in the past quarter from SR Inc COO David Osborn and updates from Andy Smith, Senior Energy Manager on the Global Energy Management and Sustainability team at Cisco Systems.
David Osborn first reflected on Apple CEO Tim Cook’s speech in late 2019 to fellow executives: “If you are an executive who has not developed an innovation strategy to address your impact on the climate, then you are failing in your responsibility as a leader.” Cook was addressing the 30th anniversary celebration of Ceres, a non-profit working for more sustainable capital markets, because, as he also said: “It’s our most successful, innovative and agile companies that have a responsibility to lead on climate and sustainability because they have the greatest capacity to act in a transformative way.”
Microsoft clearly took this message to heart when it released its new, potentially game-changing climate framework in early 2020. It announced that it would 1) become carbon negative by 2030 and net zero for all legacy emissions by 2050, 2) launch a $1 Billion climate innovation fund to accelerate the global development of carbon reduction, capture, and removal technologies among suppliers and customers, and 3) support public policy to help accelerate a net zero economy.
Other important milestones in this area came from the Science-Based Target Initiative and RE100: SBTi recently crossed the threshold of 840 companies committing to keeping global warming to well below 2 degrees and RE100 surpassed 225 companies committing to 100% renewable electricity. Additionally, the Renewable Energy Buyers Alliance (REBA), of which SR Inc is a proud sponsor, has tracked the accelerating corporate procurement of new large-scale off-site renewable energy. Through 2019, there were significantly more of these renewable energy deals than in any previous year (see Figure 1). This recent growth has been driven by not just IT companies like Google and Facebook, but also consumer discretionary and consumer staples companies like Ball, General Mills, and Walmart.
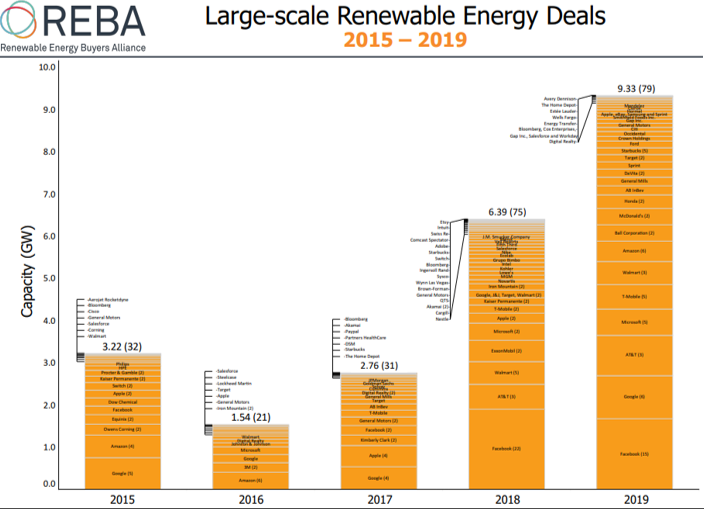
This rapid growth in large-scale off-site renewable energy procurement has not been limited to the U.S: Bloomberg New Energy Finance reports that the 19.5 GW of off-site clean energy contracts signed by over 100 corporations in 23 countries in 2019 is a new record (see Figure 2). These developments reflect the acknowledgement by most leading companies that they cannot rely on Unbundled RECs to reach their renewable energy commitments. For example, in a recent blog post, Adobe spoke about its 100% renewable energy by 2035 goal and claimed, “Adobe has been an outspoken advocate along with NGO partners such as WRI and Ceres, as well as like-minded peers, to encourage all companies to reduce and ultimately stop the purchase of offsets and Unbundled RECs and focus time, energy, and money on true grid decarbonization. We firmly believe the goal should not be to simply offset our carbon footprint, but to fundamentally change it.”


We then turned it over to Andy Smith of Cisco Systems, who provided updates on Cisco’s global energy management and sustainability efforts. Sustainability is embedded throughout the company, but its CSR and sustainability program is organized into three main pillars:
- People: Empowering employees to make Cisco an environmentally sustainable place to work
- Society: Amplifying Cisco’s sustainable practices through partnerships
- Planet: Keeping Cisco at the forefront of energy and environmental sustainability leadership
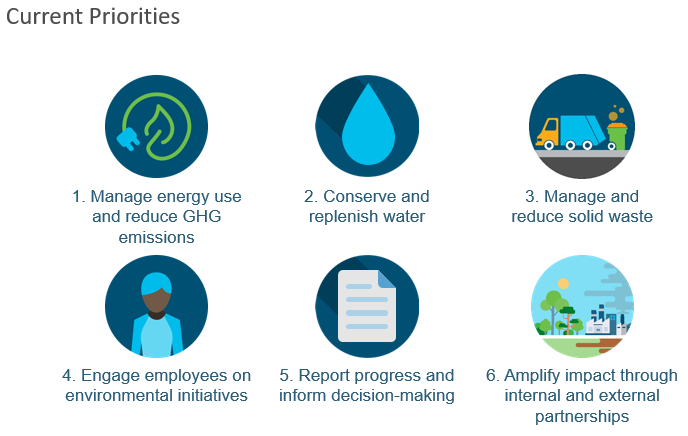
Andy’s team in particular is responsible for leading energy and sustainability efforts across the company’s physical footprint and has six main priorities (see Figure 3):
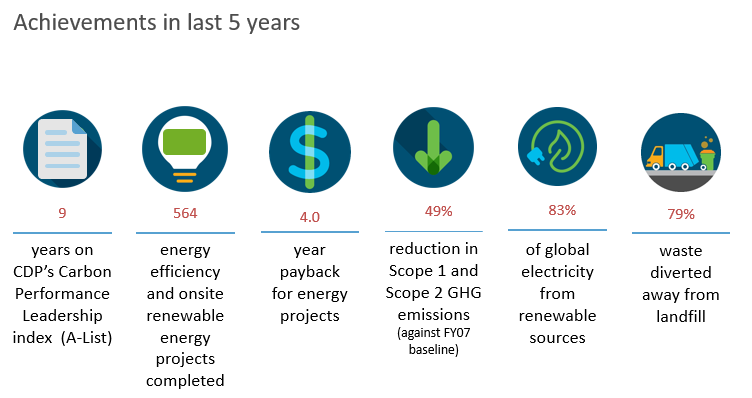
Although his team is currently developing new goals for 2030, the two main goals that have guided his recent efforts include reducing scope 1 & 2 GHG emissions worldwide by 60% and procuring 85% renewable electricity by FY2022. By the end of FY2019, Cisco reduced scope 1 & 2 emissions by 49% and achieved 83% renewable electricity. To meet these goals, Cisco has increased flexible working opportunities by investing in a connected workplace more aligned with employee work trends, has completed nearly 600 energy efficiency and on-site renewable energy projects and has signed VPPAs in California, Texas, and in India (see Figure 4). Despite an increase in workforce in the 5 years, due to its investments in connected workplace technologies, Cisco has been able to reduce its total square footage, which has aided the company’s emission reduction efforts. Additionally, his team has piloted many sustainability efforts like zero waste, water neutrality, and 100% renewable electricity at Cisco’s second largest U.S. campus in Research Triangle Park, North Carolina.
Energy efficiency has also been very important to Cisco’s current set of goals. By reducing demand, Cisco has reduced the amount of renewable energy it needs to procure. Although historically reliant on Unbundled RECs, Cisco has been procuring renewable energy since the early 2000s and has started pursuing innovative procurements like green power contracts with utilities and VPPAs in the markets where it makes the most sense. For example, Cisco contracted for a 20 MW solar VPPA in southern California in 2015 and SR Inc REPS was pleased to assist Cisco in joining with Intuit to create a market leading aggregated VPPA in ERCOT for 10 MW of wind in Texas in late 2018. Additionally, Cisco’s Bangalore, India campus is now 40% powered by solar through a two-site solar VPPA, which was one of the first and largest projects of its kind in all of India. These projects did not just save Cisco money on energy, reduce energy price volatility, and lower the company’s carbon footprint; they also created local jobs and added clean power to the Indian electric grid, which is critical considering around 75% of the power in India is generated from carbon-intensive coal-fired power plants.
Andy finished his presentation by discussing Cisco’s supply chain sustainability efforts, which are crucial to Cisco since its Scope 3 is significantly larger than its own footprint. Cisco set a supply chain emissions goal in 2016 to avoid one million metric tons of GHG emissions by 2020. In August 2019, the company met this goal and announced a new goal to reduce upstream supply chain GHG emissions 30% by 2030 and that 80% of Cisco’s key suppliers would have public GHG emissions targets by 2025. The sustainability team is working directly with suppliers to help them pursue energy efficiency projects and renewable energy in the areas that they operate. For the suppliers that operate in the same areas as Cisco, they are also exploring opportunities for partnerships such as aggregated VPPAs.

