November 25, 2025
NZCB European VPPA Opportunity Index: 2025 Q3
Executive Summary
The Net Zero Consortium for Buyers (NZCB) is continuing to assess the wide range of renewable virtual and physical power purchase agreement (VPPA and PPA) opportunities in Europe. This index is formed using recent VPPA offers and rigorous financial modelling mirroring our approach in our U.S. VPPA Opportunity Index published since 2019 (our Q3 U.S. index can be found here).
VPPA Prices are falling
In Q3 2025, average solar VPPA offer prices fell 19.4% year-over-year to €34.25/MWh, while wind prices declined 5.6% to €52.75/MWh, reflecting continued competition (SR Inc’s most recent Europe RFP received 534 proposals), market cannibalization and shifting investor focus toward hybrid and storage-backed assets. Battery energy storage system (BESS) deployment surged, with 4.6 GW contracted in H1, triple 2024 levels—led by Germany’s incentives and strong price spreads.
Wind projects offer positive modeled returns
Despite higher relative PPA prices, wind projects continue to outperform solar, offering positive modeled returns across key markets such as Romania, Finland, Spain, and Portugal. The NZCB continues to advance aggregated procurements across Europe, driving new renewable capacity while securing buyer-favorable terms for high-credit corporate members.
Demand is rising
Corporate demand for clean energy remains robust, fueled by clean energy needs for AI-driven data center growth and rising Scope 2 reduction commitments under EU taxonomy and CSRD guidelines.
Introduction
The NZCB aids corporates in our confidential renewable energy buyers’ community creating buyer-favorable transactions. It enables enterprises to chart a cost-effective path to Net Zero emissions globally while democratizing the financial and environmental benefits of utility scale clean energy.
To better quantify European VPPA market dynamics, the NZCB has launched its first quarterly European opportunity index to help advance SR Inc’s mission to accelerate the development and adoption of best practices in more sustainable business.
Like in the U.S., the NZCB VPPA Opportunity Index enables comparison of the modeled wind and solar VPPA financial performance across Europe using a consistent framework based on proprietary SR Inc analytics and data, including contributions from partners like LevelTen Energy and Pexapark. It reflects actual historical data and modeled forward pricing. Noteworthily, the Index is based upon recent VPPA offers, not executed transactions, made over the prior quarter. However, to be conservative in our estimates, we use top quartile pricing to best reflect an estimate of closing transactions
Europe stands at the forefront of global decarbonization efforts within the energy sector. Its leadership is demonstrated through innovative subsidies, national renewable energy auctions, and commercial incentives like contracts for differences, all of which set a precedent for worldwide climate action.
Increasingly, companies are entering into VPPAs to catalyze the construction of new renewable energy projects and achieve their companies’ emissions reduction targets in a high impact and low risk manner. The risk-hedging and financial benefits from corporate (V)PPAs are now seen as essential in catalysing renewable energy development. In fact, 20-25% of new renewable energy projects were backed by long-term PPAs in Europe. 
VPPAs especially are growing across the Association of Issuing Bodies (AIB) region driven by companies aiming to meet decarbonization targets. The market for virtual PPAs has grown steadily, comprising 17% of PPAs in 2025, as of May. Specific incentives for the VPPA are growing, and their value remains strong for companies looking to mitigate their Scope 2 emissions in accordance with EU taxonomy and Corporate CSRD guidelines.
For companies aiming to reduce Scope 2 emissions across Europe, the AIB membership region offers a streamlined solution. This region operates as a unified market for guarantees of origin (GOs), which are European energy attribute certificates (EACs). These GOs are currently recognized by RE100, the Greenhouse Gas Protocol (GHGP), and Science Based Targets Initiative (SBTi) and can be traded across the AIB. This means that GOs generated from projects anywhere within the AIB can now be applied to energy consumption throughout the entire AIB region, although the GHGP and SBTi are contemplating refining the market boundaries where GOs can be applied.
PPA Trends
In Q3 2025, P25 (top quartile) solar PPA price offers fell to €34.25/MWh on average across Europe, down 19.4% from Q3 2024 (note that low-priced Spanish solar is heavily represented in this average). As trends of price cannibalization in high penetration solar markets increase, standalone solar assets are looking less favorable to corporates even as solar PPA price offers decrease for a second quarter in a row.
P25 wind price offers in Q3 also declined to a P25 of €52.75, down 5.6% from Q3 2024 (note that low-priced Nordic wind is heavily represented in this average). France and Italy experienced the highest average wind PPA price offers, €80.31 in France, and €89.33 in Italy. Q3’s wind market is showing resilience as wind battles with price cannibalization less than solar does.
The volume of PPAs varied across the continent. Overall, PPAs accounted for only 6.08 GW contracted in H1 2025, marking a 26% decrease from the same period in 2024. In Germany, offtake activity saw a remarkable decrease of 84% down from 2024. Meanwhile, in Spain and Italy, solar PPA activity spiked, growing 184% year-on-year in Italy. This can be attributed to the adjustment to cannibalization and lower valuation of solar production in countries that have high solar concentration.
Electricity Demand Growth
While demand from the industrial sector has been more dormant than expected, the AI boom has resulted in significant energy demand and investment in countries such as Finland, Spain, and Ireland. In fact, data centers are now accounting for a third of new renewable PPAs in Europe. As IT companies continue to migrate data to public and hybrid clouds, new compute capacity will be required to meet this demand. Specifically, AI training and operation accounts for the largest incremental load to data centers, as AI clusters consume 25% more power per operation than conventional data center workloads.
Data center PPA consumption is expected to increase by 20 GW by 2035, and the Nordics and Italy will likely be the most popular region for new capacity, primarily due to relatively fast grid connection speeds of under three years on average. The Nordics especially are attractive to data centers because of their land availability, low temperatures, and renewable energy resource abundance. Finland is already seeing significant investment and had the greatest number of wind offers on Level Ten in 2025 so far.
Regulatory Changes
A major change in the European energy landscape is an EU-mandated shift to 15-minute time intervals, which began on September 30th. Because of the increased granularity, the quarter-hour increments allow for more accurate pricing, which paves the path for variable generation renewables to better incorporate into the wholesale markets. This also creates an opportunity for BESS systems to profit off of the dispatchable balancing services that they provide, as this will be needed on more granular levels. As settlements will now be based on 15 minute intervals, the opportunity for arbitrage within a single day increases, and so can the spread between high and low prices. The shift to quarter-hour intervals helps align the European day-ahead market with the intraday and balancing markets which already operated on 15-minute intervals. The hope is that this would help reduce negative pricing by shifting the generation curve of solar and wind assets, and allow more renewable energy to enter the market.
In Q3, Spain enacted Royal Decree-Law 7/2025, approving urgent measures designed to fortify the electricity system, directly addressing the widespread blackout experienced in April. The comprehensive legislation introduces several key provisions: First, hybrid projects are now officially recognized as fulfilling a public utility and are thereby exempted from standard environmental impact statements or declarations of public interest. Second, the planning review period for the transmission grid has been reduced from six years to three years. And finally, a robust, Spain-wide voltage monitoring service will be implemented.
BESS Updates and German Market Spotlight
To counter the trends of solar cannibalization, hybrid or co-located BESSare rapidly increasing in Europe. In H1 alone of 2025, the amount of BESS deals reached 4.6 GW (producing 9.2 GWh/year) representing more than triple the amount contracted in 2024 (1.6 GW/3 GWh).
Germany is the most advanced AIB European BESS market, due to its renewable energy penetration, arbitrage opportunities, and government incentives. Since German day-ahead prices are extremely high due to its reliance on gas, significant profit opportunities are presented for BESS investors. In fact, since the beginning of 2024, day-ahead prices have been twice as high in Germany as in Spain, the UK, and France, resulting in larger price spreads and higher arbitrage revenue opportunities for storage.
Additionally, the reliance of the intraday market accounts for further arbitrage opportunities. Dispatchable batteries are highly valuable since Germany relies on the intraday market for 15-20% of its energy trading, compared to 5% in other AIB countries. Finally, Germany offers access to the primary, Frequency Containment Reserve (FCR), and secondary, automatic Frequency Restoration Reserve (aFRR), which provide additional profit for BESS.
Germany also employs a national “Innovation Auction” to promote onsite BESS for constrained projects (those that only charge from a hybrid solar or wind asset). This auction has succeeded in driving 700 MW of solar-plus-storage projects since 2021.
Although there are many tailwinds in the German BESS market, some changes are on the horizon. While ancillary services market revenues are expected to rise in the short term, in the medium-term, between 2028-2029, they are now forecasted to decline and be outpaced by intraday and day-ahead revenue due to the saturation of storage in Germany. This trend was foreseen in the German market, but its onset is faster than was initially anticipated by energy experts.
However, regulatory progress for storage in Germany has not advanced without complications. For example, the Baukostenzuschuss construction fee which large electricity consumers have to pay to the distribution system operators (DSO), intended to charge large energy users to help fund grid infrastructure. A high German court recently ruled that BESS projects are also required to pay this fee, despite their dual-function as producers and consumers.
While other European countries also explore reduced grid tariffs and other incentives to increase BESS capacity and help with load balancing, subsidy schemes remain the main driver of co-located battery deals, resulting in BESS PPA deals’ growth at a higher rate than overall standalone PPA growth. Subsidies vary in type, and while countries like Spain, Portugal, and Bulgaria offer upfront capex grants, others including Germany offer operating subsidies in the form of a market premium, where the state guarantees a minimum remuneration. These are used by large utility-scale renewable energy producers to make a better case for profitability and risk minimization.
Two significant regulatory challenges create friction for BESS developers. The first is the permitting rules surrounding grid charging can often be tedious. The second is the double grid fees that many countries still impose on storage assets for intake and output of electricity to the network. Schemes like the French TURPE-7 are aimed at eliminating some of these hurdles, as regulations calibrate to accept the integration of more storage on the grid.
Overall, the arbitrage opportunities for BESS provide a compelling opportunity for co-located solar and wind, especially in markets with high solar proliferation. Germany, as the most advanced BESS market in AIB Europe, still incentivizes new storage, but expects increasing saturation in the next decade which will shift the revenue sources for co-located solar and wind. Other countries, with more nascent BESS markets, are devising new laws and regulations to promote the financial case for storage, and mitigate existing hurdles.
Negative Pricing Calls for Diligent Contracting
Previously the exemplary renewables landscape, the Spanish market is facing bottlenecks that create difficulties in adding new capacity. Trends of extreme cannibalization and episodes of intense negative pricing that were previously unexpected have led offtakers to suffer from low capture prices and hesitate on future investments.
Recently, about 90% of industrial grid access applications in Spain have been rejected due to infrastructure inadequacy. Continuing trends of cannibalization are reducing price expectations for standalone solar in Spain as well. Offtakers are seeing losses in what was initially a highly profitable market. Spanish solar earned €33.50/MWh on average in Q3, down 10% from last year.
Despite these headwinds, Spain continues to be a popular market for investment, as data centers increase demand, and carefully tailored VPPA contracts aim to circumvent these hurdles. Spanish government incentives aim to reach 22.5 GW of BESS assets by 2030 to help combat negative pricing. One example of a government incentive supporting this is a €700 million support scheme encouraging the development of new storage systems including co-located BESS and pumped hydro.
Amidst uncertainty, Spain prevails as a leader in the renewables landscape, and even accounted for 30% of PPA offers in AIB proposed through SR Inc’s partner LevelTen Energy this year. As corporate offtakers gain experience, terms and technologies to protect buyer interests are increasing in prevalence in VPPA contracts. These include setting non-settlement thresholds, presupposing maximum curtailment hours, offtaking wind (which suffers far less from cannibalization), and combining solar, wind, and batteries for more balanced output.
The NZCB employs a highly specialized and dynamic Letter of Intent (LOI) and Term Sheet (TS) that factors in buyer-favorable terms to mitigate many of the risks associated with variable generation and negative pricing. It is specifically intended for the high-credit corporate buyer, and is optimized by geography. It includes an assumed €0 price floor, so offtakers do not have to take on liability for indefinite negative pricing. Also included are strict limitations on curtailment, and damages for underperformance, meant to hedge against risks that buyers face in increasingly saturated markets. Offtakers trust the NZCB LOI and TS to represent their risk-averse requirements, while aiming to mitigate their Scope 2 emissions in the most impactful way.
SR Inc’s Experience on VPPAs in Europe
SR Inc’s NZCB has been active in Europe’s VPPA market for the past several years. Through our aggregated procurement model, we have combined the demand of companies looking to mitigate load across AIB Europe.
In 2023, the NZCB facilitated a 127MW Aggregated Procurement on a solar project in Spain with Thermo Fisher Scientific and Eurofins Scientific. Through this partnership, both companies are able to mitigate their scope 2 and 3 emissions. Eurofins, as a supplier and customer of Thermo Fisher achieved Scope 2 reductions, while simultaneously reducing Thermo Fisher’s Scope 3 emissions.
Earlier this year four NZCB participants completed another aggregated procurement in Europe. Autodesk, Synopsys, IDEXX, and another NZCB participant each committed 5-13 MW of the 50 MW Catania Solar project in Italy. By combining their demand, and streamlining the contract finalization through one negotiation process, the consortium was able to cause a new solar project to be built in Italy and contribute to the emergence of VPPAs in Europe.
Looking forward, the NZCB is arranging other aggregated procurements in Europe AIB, Poland, and the UK this year. In fact, the supply of well-priced offers in Europe has never been higher. We received the most proposals in our AIB Europe RFP (request for proposals) that the NZCB has seen. Our finalists include solar, wind, combo (solar and wind), and hybrid (asset plus battery) proposals that are competing to become the prevailing proposal.
Top proposals span the whole continent, with a few notable market clusters. The Nordics (specifically Finland and Sweden) stand out in hybrid and standalone wind offerings due to their market maturity, their commitment to increasing transmission capacity, and expected growth in demand due to a proliferation of industry load in data centers and green hydrogen production. The second market cluster is comprised of German hybrids which stand out due to the German developers’ experience with co-located BESS, more attractive bankability for hybrid projects, and significant demand increases expected with industrial electrification (see German BESS section above).
SR Inc’s Q3 2025 Financial Evaluation
In Q3, SR Inc’s analysis shows that Europe faced vast declines in solar PPA offer prices, on average shrinking by 10% across the continent since Q3 2024. The decline of solar PPA prices can be attributed to the continuation of cannibalization, especially in markets with significant solar penetration. Wind maintained the same level of demand as a year earlier averaging a decline of just 0.1%.
Using both historical and forecasted data, SR Inc’s analysis shows that average VPPA settlement prices across active hubs was €57.55/MWh through term for solar and €70.05/MWh for wind (ranging from €41.86/MWh for Spanish solar to €87.97 for Romanian wind).
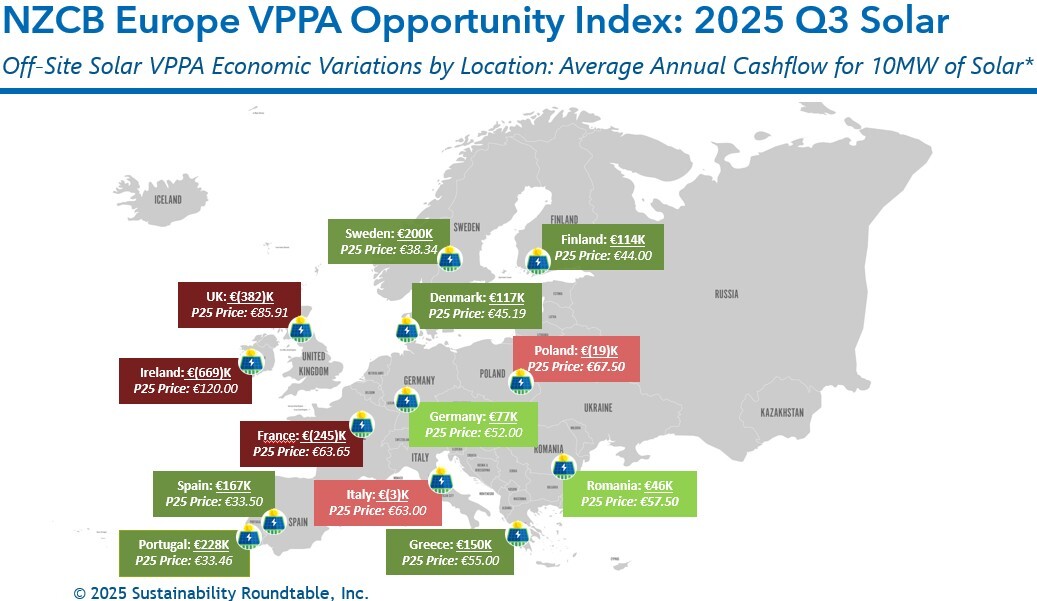
As shown in the below graphic, our solar PPA forecasting shows that Portugal, Sweden, Spain, and Greece were the best markets for stand-alone solar in Q3, earning expected positive cashflows of €228K, €200K, €167K, and €150K, respectively, for a modeled 10MW offtake. Solar was the dominant technology in PPA offers, though because of oversaturation, revenue expectations are declining, as demand lags behind supply. In fact, the average expected settlement on a 10MW modeled solar offtake across the European markets we analyzed was a loss of €17K.
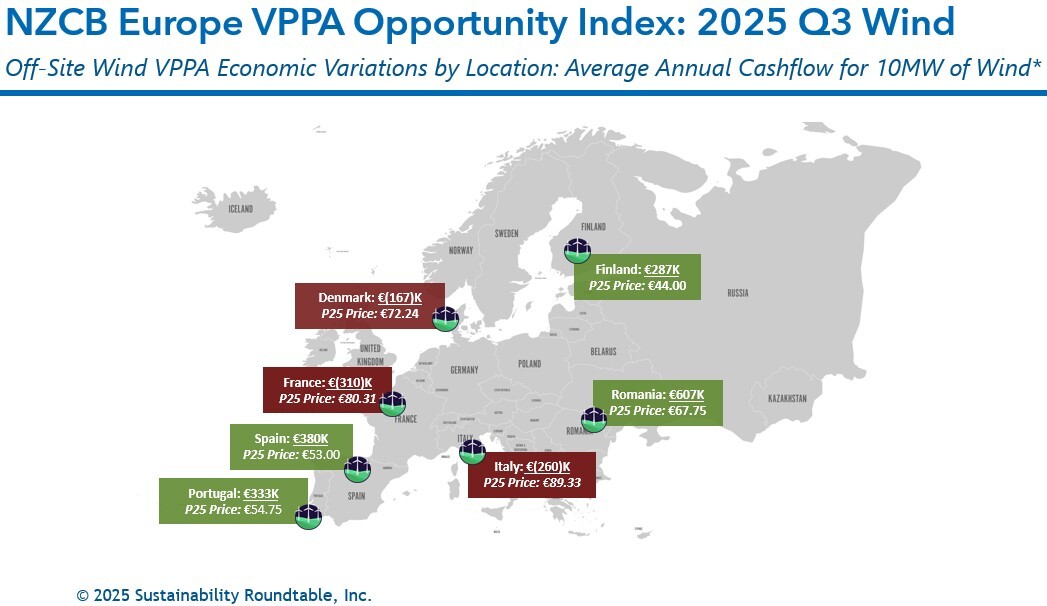
As shown in the below graphic, price modeling shows that Romanian, Spanish, Portuguese, and Finnish wind projects provide the greatest opportunities for positive cashflow in Q3, with our models showing average annual positive cashflows of €607K, €380K, €333K, and €287K, respectively, for a 10MW offtake. Wind projects remain less represented than solar in overall PPA offers across Europe, but provide a more favorable generation profile than solar. The average expected settlement on a 10MW modeled wind offtake across the European markets we analyzed was a gain of €124K.
*Methodology
- To calculate average annual cashflows, SR Inc multiplies 1) the difference of historical backcast data and forecasted technology-shaped electricity futures market prices (2026-2040) versus top quartile VPPA prices in each hub by 2) the typical total annual production for 10MW offtakes for wind and solar, respectively.
- SR Inc uses 30K MWh production per year for 10MW of wind in Europe and 20K MWh per year for 10MW of solar in Europe to provide “apples-to-apples” comparisons for both technologies across hubs.
- The top quartile VPPA price typically assumes a scaled offtake of at least 30MW, but SR Inc uses 10MW because it is a typical minimum individual corporate offtake required within aggregated procurements for NZCB participants.
- Our solar analysis is based on LevelTen P25 data from Bulgaria, Croatia, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Spain, Sweden, and the United Kingdom.
- Wind analysis includes LevelTen P25 data on Finland, Germany, Greece, Italy, Poland, Portugal, Sweden, and the UK.
Data Sources
- The NZCB Opportunity Index is developed from proprietary analytics and multiple data providers, which include:
- LevelTen Energy PPA Price Index North America top quartile VPPA pricing data for Q3 2025 (all proposed projects of 8+ years)
- LevelTen Energy Marketplace actual average, technology-shaped realized market prices for 2018- June 2025 (excluding 2022, which stands as an outlier with very high prices due to the war in Ukraine) and the default technology-shaped future market price forecasts for 2026-2040 (as of October 20, 2025).
